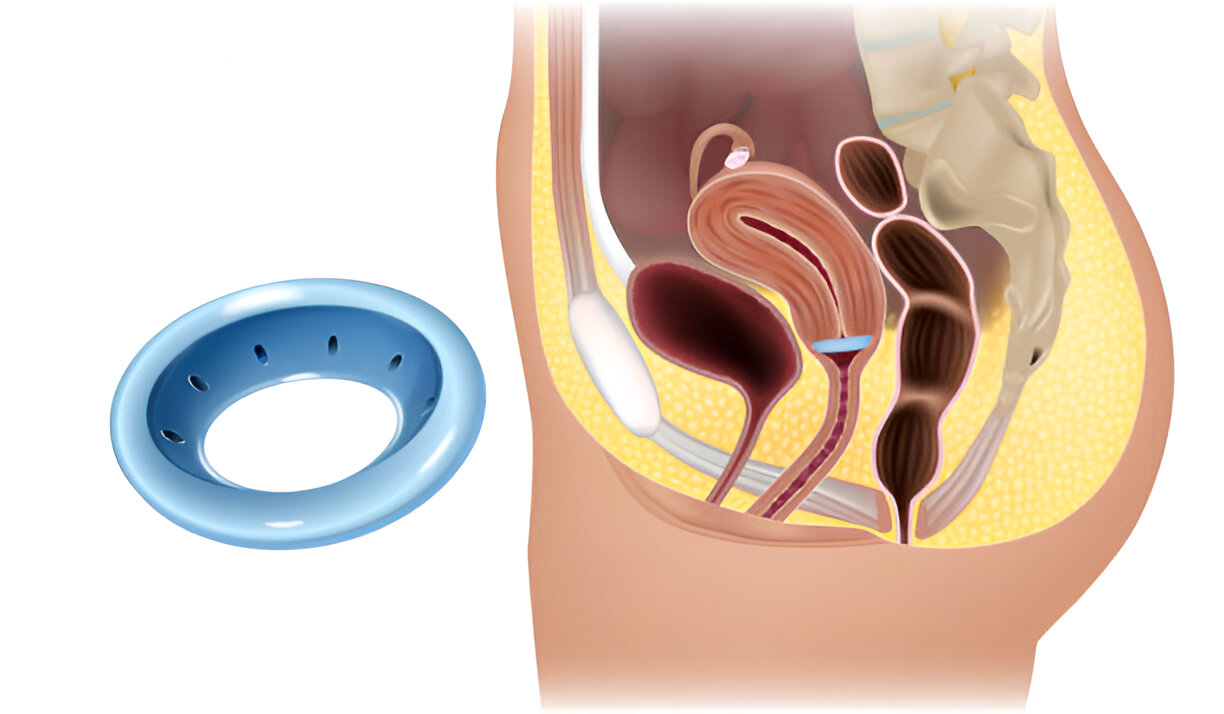
Uterine/Vaginal Prolapse
A benign gynecological disorder is a non cancerous condition affecting the female reproductive system such as uterine fibroids and endometriosis. The condition can cause discomfort, pain and various other symptoms which are generally not deadly.
Symptoms
- A feeling of fullness or pressure in the pelvis and vagina
- Visible or palpable bulge of tissue protruding from the vagina
- Difficulty with bowel movements
- Urinary incontinence or retention
- Painful intercourse
- Lower back pain
- Vaginal bleeding or discharge
Causes
- Childbirth: Vaginal delivery, especially of large babies, can weaken pelvic muscles.
- Aging: Loss of estrogen after menopause can weaken the pelvic floor.
- Hysterectomy: Removal of the uterus can lead to prolapse of other pelvic organs.
- Chronic coughing: Conditions like bronchitis or asthma.
- Obesity: Extra weight increases pressure on the pelvic floor.
- Heavy lifting: Strain from repetitive heavy lifting.
- Chronic constipation: Straining during bowel movements can weaken pelvic muscles.
What are the Treatment options : ?
Non-surgical Treatments:
- Pelvic Floor Exercises (Kegels): Strengthening the pelvic muscles.
- Pessary: A device inserted into the vagina to support the uterus.
- Lifestyle Changes: Weight management, avoiding heavy lifting, treating constipation.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy: Estrogen therapy to strengthen pelvic tissues.
-
Surgical Treatments:
- Vaginal Repair Surgery: Rebuilding the pelvic floor and reattaching the prolapsed organs.
- Hysterectomy: Removal of the uterus in severe cases.
- Sacrocolpopexy: Surgical attachment of the vagina to the sacrum (lower back).
- Colpocleisis: Closure of the vaginal opening in non-sexually active women
Health Care Tips?
- Regular Exercise: Engage in pelvic floor exercises to strengthen muscles.
- Healthy Diet: Consume a high-fiber diet to prevent constipation.
- Weight Management: Maintain a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the pelvic floor.
- Avoid Heavy Lifting: Minimize activities that strain the pelvic muscles.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to promote regular bowel movements.
- Regular Check-ups: Visit your healthcare provider regularly to monitor and manage symptoms
How It Works?
Maintaining a healthy weight, performing regular pelvic floor exercises, and avoiding heavy lifting can help prevent uterine prolapse.
It is relatively common, especially among women who have had multiple vaginal deliveries or are postmenopausal.