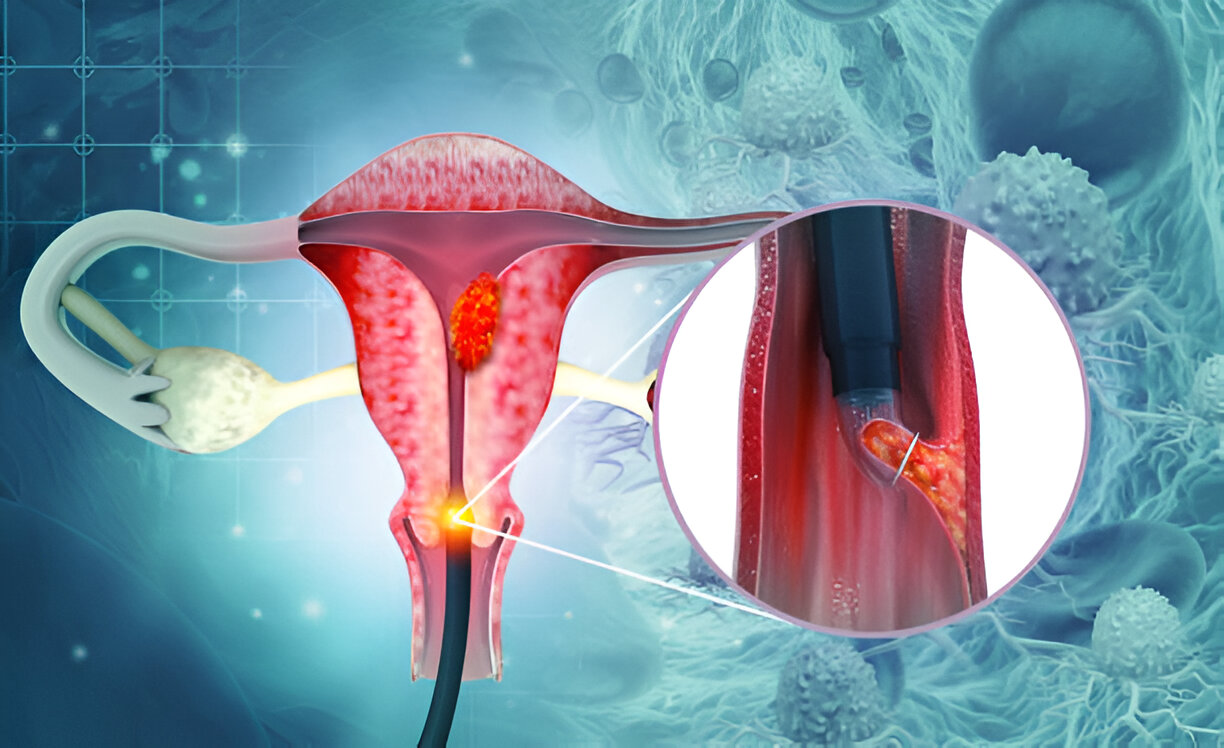
Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure used to examine the inside of the uterus. It involves the use of a hysteroscope, a thin, lighted tube that is inserted through the vagina and cervix into the uterus. This procedure can be diagnostic or operative.
Diagnostic Hysteroscopy
Definition: Diagnostic hysteroscopy is performed to diagnose uterine abnormalities. It allows the doctor to view the inside of the uterus to identify the cause of various symptoms.
Indications:
- Abnormal uterine bleeding
- Unexplained infertility
- Repeated miscarriages
- Evaluation of uterine polyps or fibroids
- Investigation of congenital uterine anomalies
- Postmenopausal bleeding
Procedure:
- Preparation: The patient may receive a local, regional, or general anesthetic.
- Insertion: The hysteroscope is gently inserted through the vagina and cervix into the uterus.
- Inspection: Saline solution is often used to expand the uterus, allowing for a clear view.
- Diagnosis: The doctor examines the uterine lining and may take biopsies for further analysis.
Benefits:
- Minimally invasive with quick recovery
- Accurate diagnosis of uterine conditions
- Can be done in an outpatient setting
Operative Hysteroscopy
Definition: Operative hysteroscopy is used to treat abnormalities identified during diagnostic hysteroscopy. It involves using specialized instruments passed through the hysteroscope.
Indications:
- Removal of uterine polyps and fibroids
- Cutting adhesions (Asherman's syndrome)
- Treating uterine septa
- Endometrial ablation
- Removing retained products of conception
Benefits:
- Minimally invasive with shorter recovery time compared to open surgery
- Precise treatment of uterine conditions
- Reduced risk of complications and scarring
What are the Treatment options : ?
- Surgery: Removal of cancerous tissues or organs.
- Radiation Therapy: Using high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Using drugs to destroy cancer cells throughout the body.
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs that target specific molecules involved in cancer growth.
- Immunotherapy: Boosting the body's immune system to fight cancer cells.
- Rest: Take it easy for the first 24 hours after the procedure.
- Avoid Intercourse: Refrain from sexual activity for at least a week or as advised by your doctor.
- Monitor Symptoms: Watch for any signs of infection, such as fever, severe pain, or heavy bleeding, and report them to your doctor.
- Follow-Up: Attend any scheduled follow-up appointments to ensure proper healing and to discuss the results.
- Hydration and Diet: Stay hydrated and maintain a healthy diet to support recovery.
Health Care Tips Post-Hysteroscopy
How It Works?
A1: Most patients experience minimal discomfort. Anesthesia is used to ensure comfort during the procedure.
A2: The procedure typically takes between 15 to 30 minutes, depending on whether it is diagnostic or operative.